- HOME
- PRODUCTS
- SUPPORT
Support
Get useful and free tools, sources and professional buyer guides to make good choices of products.
Ordering Guide
How to Buy
- ABOUT USPP-LINK is a leading network supplier, providing enterprise customers and end-users professional ICT products and solutions.
- CONTACT US

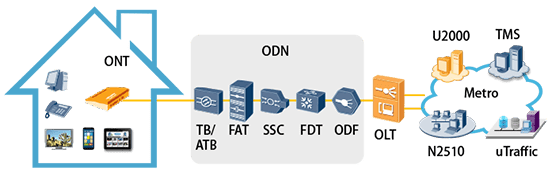
FTTH solution uses one optical fiber network to bear multiple services, providing high speed Internet (HSI), Wi-Fi, voice, video, and CATV services for home-connected users. This superior solution removes the bottleneck between homes and the backbone network to implement its ultra-broadband architecture and simple, flattened network structure, facilitating easy deployment and O&M.
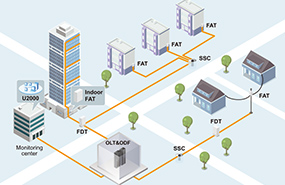
Outside plant
OSP is any network infrastructure installed external to buildings. Scope includes optical fiber cabling, balanced twisted-pair cabling, and support assemblies FDT,FAT,Closure and so on of the network node which carrying the network service.
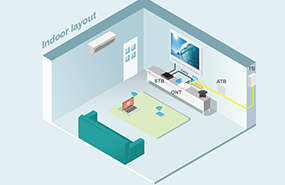
Inside plant
ISP refers to cable and devices installed inside of the building. This includes everything from the patch panel, patch cord, TB,ATB,STB,ONT and switch to the cables and jacks which finishing the network access to end users.
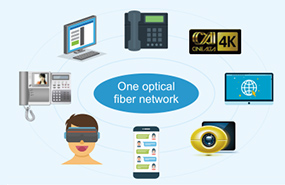
A Single Optical Network That Bears Multiple Services
Network environments have changed: multi-service networks have become a trend, enabling every household network to bear multiple services.

Deployment and O&M Face New Challenges
Optical fibers are routed to maximize coverage and reach as many users as possible, requiring networks to be simpler and easier to deploy, operate, and maintain.
FTTH Typical Networking
FTTH has the following three typical networking models. SFU ONT can be regarded as a pipe providing L2 data and voice services. HGW ONT provides L3 services; it is the center of a manageable home network and can be regarded as the "tap" of the smart pipe.
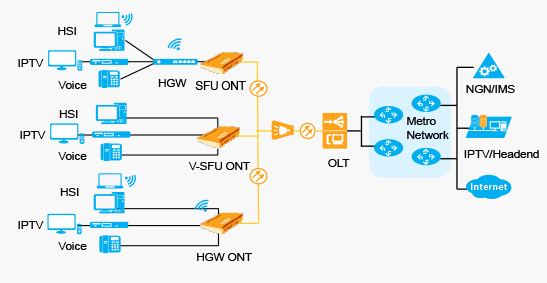
Bridging-type ONT+HGW
Equipped with a built-in IAD, HGW provides users with Internet access, VoIP, and IPTV services. The bridging-type ONT works with the OLT to provide L2 channels.
Bridging+Voice-type ONT
Equipped with a built-in IAD, the ONT provides users with L2 data services and voice services. This scenario provides transparent transmission channels and requires simple service configuration, so this scenario applies to L2 networking.
Gateway-type ONT
Equipped with a built-in IAD, the ONT provides services to users. The gateway-type ONT can provide L3 services such as DHCP/ PPPoE dial- up, NAT, and IGMP snooping, facilitating device interconnection in a house.
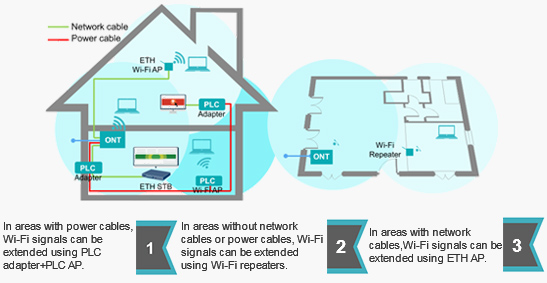
Wi-Fi Coverage for Homes
ONTs with Wi-Fi capabilities can address the needs of most households for Wi-Fi services. However, for large houses or villas, a single ONT cannot provide indoor Wi-Fi coverage for the entire house.
Acronyms and Abbreviations
AP | access point | BNG | broadband network gateway |
EPC | evolved packet core | EMS | element management system |
FTTB | fiber to the building | FTTC | fiber to the curb |
eOTDR | embedded optical time domain reflectometer | FAT | fiber access terminal |
FDT | fiber distribution terminal | FTTH | fiber to the home |
HGU | home gateway unit | IAD | integrated access device |
ITMS | intelligent terminal management system | LTE | long term evolution |
OAM | operation, administration and maintenance | ODF | optical distribution frame |
ODN | optical distribution network | OMCI | optical network terminal management and control interface |
OTDR | optical time domain reflectometer | OSS | operations support system |
OTT | over the top | PLC | power line communication |
RAN | radio access network | SFU | single family unit |
SNMP | simple network management protocol | TMS | terminal management system |
WAN | wide area network |
About
Support



